Foam is an incredibly diverse material, with hundreds of types, classifications, and formulations available. This variety exists because even a minor change in the chemical composition can drastically alter the foam’s structure, behavior, resistance, and performance. While entire books can be written about foam science, for practical purposes—like choosing the right foam for a specific application—it helps to simplify the discussion.
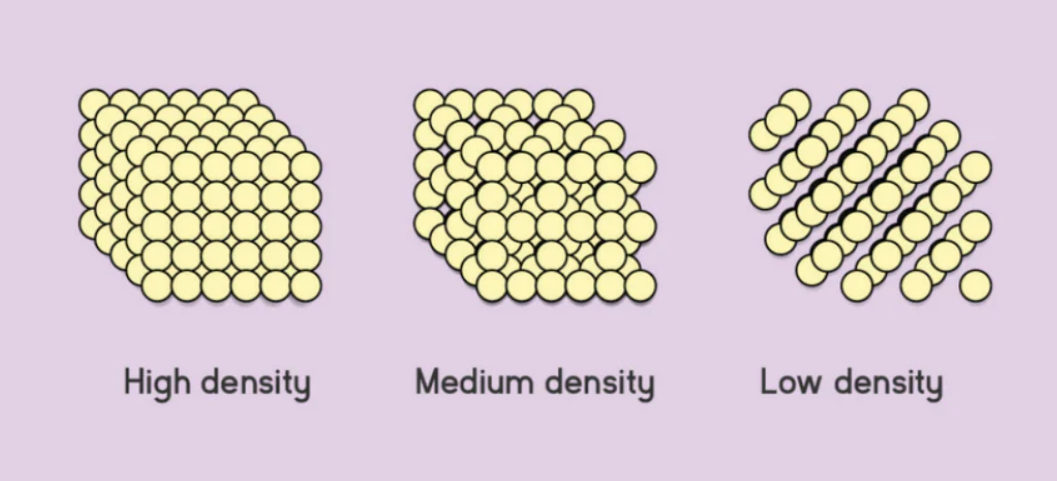
One of the most fundamental ways to categorize foam is by density. Two commonly used classifications are high-density and low-density polyurethane foams. But what exactly is foam density, and how does it affect performance?
What Is Foam Density?
Foam density refers to the mass per unit volume of the foam—essentially how compact or heavy the material is. Denser foams weigh more for the same volume and typically have smaller, more tightly packed cells.
Interestingly, foam density is not the same as firmness. A high-density foam can feel soft, while a low-density foam can be manufactured to feel quite firm. Firmness depends on the foam’s mechanical properties, not just its weight.
Factors That Affect Foam Density During Manufacturing
Two main factors influence foam density:
1. Blowing Agents
These are compounds (organic or inorganic) that generate gas bubbles during the foam’s formation. As the resin expands, the gas forms the cellular structure of the foam. The type and behavior of the blowing agent determine how much expansion occurs, directly affecting density and cell structure.
2. Chemical Additives
Additional chemicals like cell stabilizers, crosslinking agents, and fillers can further control the foam’s density and internal structure.
Cell Structure: Open vs. Closed Cell Foam
Density influences—but does not solely determine—cell structure.
Low-density foams typically have larger, more open cell structures, allowing air, gas, or liquid to pass through. These are often used in filtration, cushioning, and sound absorption.
High-density foams generally feature smaller, more compact cells, which can create a closed-cell structure that blocks moisture and gases, making them ideal for gasketing, sealing, and thermal insulation.
Note: Not all high-density foams are closed-cell, and not all low-density foams are open-cell. Cell structure depends on manufacturing methods and the specific formulation.

Applications of High-Density Polyurethane Foam
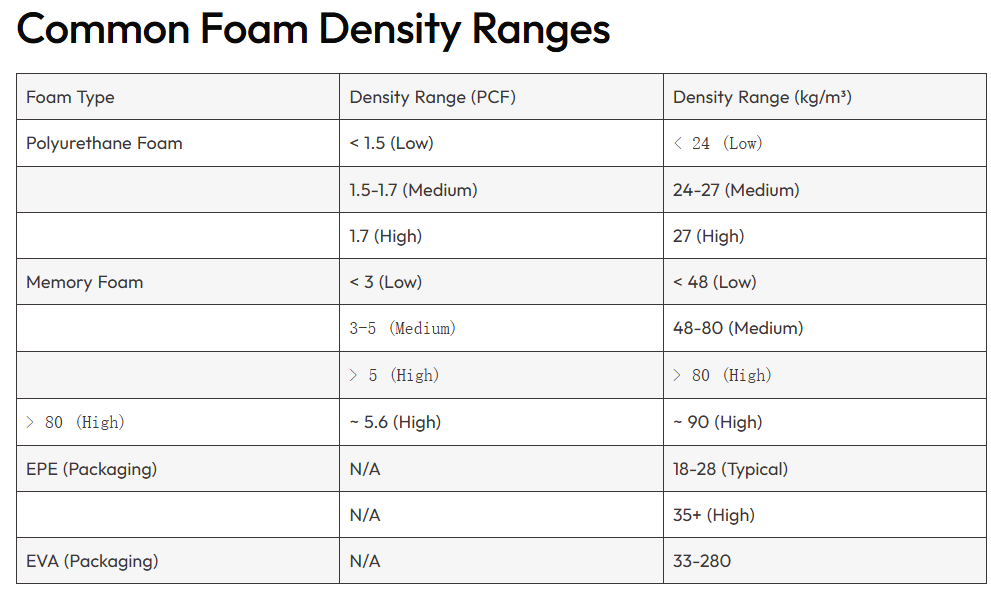
High-density polyurethane foam (typically 10–20 lbs/ft³) is often used in applications that demand durability, resilience, and resistance to environmental stressors.
Common use cases include:
Gasketing and sealing (meets UL 50 and UL 508 standards)
Vibration isolation and sound damping
Shock absorption and protective packaging
Gap-filling in assemblies and products
Thermal insulation
Mounting and spacing applications
Benefits of High-Density Foam
Exceptional durability and resilience
Greater tensile strength and tear resistance
High load-bearing capacity and shock absorption
Reduced compression set (less permanent deformation over time)
Excellent vibration and acoustic dampening
Wide service temperature range: –40°F to 194°F (–40°C to 90°C)
Good water resistance due to closed-cell construction
Chemical and ozone resistance
Low fogging (complies with SAE J-1765)
When to Use Lower Density Polyurethane Foam
Low density polyurethane foam (from about 1 to 6 lbs./ft2) is an economical open-cell foam that is generally used for filtration applications and select gasketing applications (i.e., door gaskets). The material’s primary advantage, when compared to high density foams, is its excellent compression and memory. The foam will rebound after being compressed, making it ideal for applications that experience a periodic cycle of differing amounts of compression over time.
Low density polyurethane foam offers several other advantages:
Thermal insulation: less dense foams offer higher insulating properties
The ability to be used to filter air and water
A higher cost efficiency
Excellent resilience and bounce back
Adequate sound absorption and vibration dampening
Good cushioning capabilities
Good thermal insulation and flame resistance
Thermal conductivity with a good service temperature range (-40° - 194°)
Produced in buns and long boards, these products typically will need to be skived to the specific application thickness. Once skived to thickness, these foams are also often laminated with pressure sensitive tapes and then slit into rolls or die-cut into parts.
Compression Sofas China Source Factory - KINGSEN
KINGSEN is a professional manufacturer with over 20 years of experience in designing and producing high density foam products and compressed sofas. the main prodcuts include: Modular Sectional Sofas, Sofa Beds, Bean Bag, Kids Couch & Climbing Play .etc. We supply full custom service, including developing OEM & ODM projects. all products can be customized by material, size, color, logo, and more. Our company owns 25000m2 factory area and more than 200 sets of advanced manufacturing equipments, Perfect and rigorous QC system. Also, we have passed the ISO9001: 2015, BSCI, IAF Quality Management System Certification. We look forward to your visit and the opportunity to build a successful partnership together.



